A recent debit card breach has sparked significant concern among consumers and financial institutions alike, as the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) grapples with the fallout. With reports of fraudulent withdrawals surfacing from various locations, including China and the USA, the implications of this breach extend beyond the 641 affected cardholders. The current scenario raises critical questions about the robustness of cybersecurity in India, particularly under the guidelines set forth by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). As digital transformation continues to reshape finance, the urgency to enhance cybersecurity measures has never been more pressing. In a landscape where cyber threats are evolving, it’s crucial for institutions to address these vulnerabilities to safeguard the financial data of millions.
In light of the recent incident involving compromised debit cards, the financial sector is facing increasing scrutiny regarding its security protocols. This breach highlights the vulnerabilities associated with digital finances and the need for enhanced protective measures against emerging cyber threats. With unauthorized transactions alarming consumers, it is evident that the banking system must adapt to these challenges and prioritize fraud prevention and management. These cybersecurity concerns may jeopardize the trust placed in digital banking platforms, demanding immediate attention from banking regulators and institutions. Thus, as financial transactions continue to migrate toward digital ecosystems, robust cybersecurity strategies are essential to safeguard users and uphold the integrity of the financial system.
Understanding the NPCI Debit Card Breach
The NPCI debit card breach has raised significant concerns among cardholders and financial institutions alike. Following the breach, the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has been transparent in addressing the fears of consumers, particularly by highlighting that the issues were confined to cards issued by 19 banks, affecting 641 customers. However, the potential risk extends to a much larger pool, as an estimated 3.2 million cards were at risk. This situation highlights the vulnerabilities within the existing payment system and the urgent need for stronger cybersecurity measures for digital transactions.
As we navigate through these incidents, it becomes crucial to understand the extent of the breach and why it occurred. Analysts have pointed out the need for a thorough audit of existing infrastructures, especially in light of NCC’s current audit by the Payment Card Industry Security Council. Cybersecurity experts emphasize that this breach serves as a wake-up call—not only for the banks involved but for the entire digital banking ecosystem in India, prompting an immediate reevaluation of their security systems and fraud detection strategies.
The Evolution of Cybersecurity in India
India’s journey toward a robust cybersecurity framework has been tumultuous, especially given recent breaches such as the NPCI debit card incident. Experts, including Vivek Gautam from IDC India, explain that many companies hesitate to disclose cyberattacks due to potential reputational damage. This culture of silence is rapidly changing, particularly since the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has now mandated immediate reporting of cybersecurity incidents to prevent regulatory penalties. This shift encourages transparency and can ultimately fortify the financial sector against future breaches.
Furthermore, the RBI has been proactive in pushing organizations toward implementing cybersecurity policies effectively. However, the challenge remains that many banks are lagging behind in their cybersecurity readiness. Reports suggest that while some institutions understand the necessity of robust cybersecurity measures, the implementation of these practices remains insufficient. To combat emerging threats, especially those facilitated by the Darknet, the financial sector must enhance its frameworks and continuously adapt to evolving cyber threats.
Fraudulent Withdrawals and Their Impact on Consumers
Fraudulent withdrawals can have a devastating impact on consumers, as demonstrated by the recent NPCI debit card breach. Cards from 19 banks reported unauthorized transactions, primarily overseas, leaving consumers bewildered and questioning their financial safety. Such occurrences not only affect individual consumers, who may face financial setbacks, but they also erode trust in financial institutions and systems. The handling of these incidents can either reinforce or diminish reputation and client relationships in the banking sector.
The rise in fraudulent activities necessitates a significantly sharper focus on fraud detection and management systems within Indian banks. Current infrastructures are deemed inadequate, as indicated by multiple experts in cybersecurity, pointing to a gap in effective risk management. The onus is on banks to develop user-focused solutions that prioritize security while maintaining user confidence through transparency, education, and timely communication during incidents.
RBI’s Cybersecurity Regulations: A Double-Edged Sword
The RBI’s recent directives on reporting cybersecurity incidents mark a pivotal shift towards enhanced accountability in the banking sector. By instituting stringent regulations, the RBI aims to create a safer financial environment. Yet, the imposition of such regulations could also lead to banks facing pressures that may inadvertently stifle innovation. Institutions must find a balance between compliance requirements and fostering a culture that prioritizes proactive cybersecurity measures without compromising their day-to-day operations.
Moreover, the RBI’s move has sparked discussions around the comprehensive plans banks need to implement to follow these regulations effectively. Current cybersecurity policies can be seen as merely a checklist, lacking the depth required for real-world application. There is a dire need for banks to cultivate frameworks that not only comply with RBI regulations but also enhance their overall security posture to protect against Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) and other sophisticated cybercriminal tactics.
Digital Transformation in Finance: Progress and Pitfalls
The digital transformation in India’s financial sector is viewed as a critical step toward a cashless economy. As banks and financial institutions integrate digital technologies into their operations, they face the challenge of ensuring robust cybersecurity measures are in place. The recent NPCI debit card breach highlights the foundational cracks in this transformation process, particularly concerning inadequate physical and network security for ATMs and online transactions. Stakeholders must address these vulnerabilities if they are to safeguard consumers’ data and finances in an increasingly digital age.
In parallel, the call for enhanced cybersecurity measures must not hinder innovation in the BFSI sector. Rather, a balanced approach is necessary to ensure that as the industry evolves digitally, it does so with the infrastructure to protect against rising threats. Effective communication of security measures to consumers can foster increased confidence, allowing the digital transformation to align with consumer expectations for safety and efficiency in financial transactions.
Risk Management and Cybersecurity Frameworks
Effective risk management frameworks are paramount in minimizing the adverse effects of cyber incidents within the financial sector. The shift towards more robust cybersecurity practices highlights the need for a well-defined approach that exceeds mere compliance checks. As recommended by experts, organizations should adopt risk assessment frameworks similar to NIST in the U.S. This proactive approach would allow financial institutions to independently evaluate their cybersecurity postures and implement measures to mitigate potential breaches.
Additionally, companies must commit to continuous learning and adaptation in their cybersecurity strategies. Regular audits, employee training, and the implementation of advanced security technologies can dramatically enhance an organization’s ability to detect and respond to potential threats. As the cyber landscape evolves, so too must the methodologies employed by financial institutions, ensuring they remain one step ahead of cybercriminals.
The Importance of Transparency in Cybersecurity Incidents
Transparency in reporting cybersecurity incidents is paramount in maintaining consumer trust and confidence. The NPCI debit card breach serves as a stark reminder of the repercussions of opacity in the financial sector. Proactive communication regarding breaches allows organizations to engage with customers, providing them with necessary information and reassurance. Furthermore, open discussions about vulnerabilities and breaches pave the way for collective learning and stronger defenses across the industry.
As regulatory bodies impose stricter requirements for reporting, financial institutions must embrace a culture of transparency. By openly sharing information about breaches and their aftermath, banks equip consumers with the knowledge to make informed decisions. Transparency not only aids in restoring consumer trust post-breach but also fosters a collaborative environment where industry partners can share critical intelligence to enhance cybersecurity across the entire spectrum of financial services.
Investing in Cybersecurity: The Path Forward
Investment in cybersecurity is not merely a luxury for financial institutions; it has become a necessity. The NPCI debit card breach emphasizes the importance of allocating sufficient resources toward cybersecurity initiatives. Developing resilience against fraud and cyber threats will require not only investment in advanced technology but also a cultural shift towards prioritizing security within every level of an organization. Moreover, cybersecurity should be viewed as a shared responsibility, requiring collaboration among financial institutions, technology partners, and regulatory bodies.
Furthermore, while investing in cutting-edge security products is crucial, banks must also prioritize cultivating a culture of shared cybersecurity intelligence. By establishing partnerships that focus on information sharing regarding threats and breaches, institutions can create a more unified front in combating cybercrime. Overall, a comprehensive approach—merging technology, culture, and collaboration—will be essential in shaping a secure financial future for India.
Frequently Asked Questions
What caused the recent NPCI debit card breach in India?
The recent NPCI debit card breach was reported after customers from 19 banks experienced fraudulent withdrawals, primarily in China and the USA. Although only 641 customers were directly affected, concerns arose that a total card base of approximately 3.2 million may have been compromised.
How can I protect my debit card from breaches and fraudulent withdrawals?
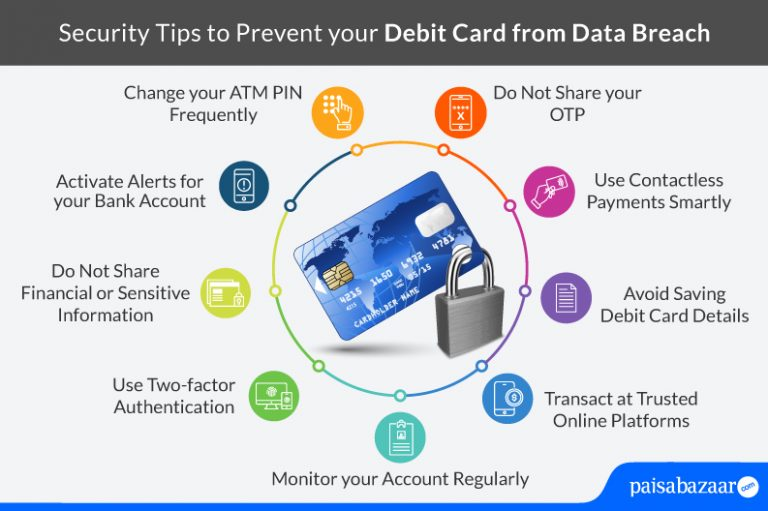
To protect your debit card from breaches, regularly monitor your account for unauthorized transactions, enable alerts for transactions, use strong passwords, and avoid public Wi-Fi when making transactions. Additionally, consider using virtual cards for online purchases to enhance security.
What steps is the RBI taking to address cybersecurity regulations in light of the recent debit card breach?
In response to the debit card breach, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has mandated that all banks report cybersecurity incidents promptly. This directive aims to enhance transparency and reinforce the importance of cybersecurity within the banking system.
How did the NPCI respond to the fears surrounding the debit card breach?
The NPCI acknowledged the panic among cardholders following the debit card breach and provided clarifications. A P Hota, the CEO of NPCI, stated that the fraudulent withdrawals were limited to specific banks and emphasized efforts to audit the breach thoroughly.
What are the implications of the debit card breach for India’s digital transformation in finance?
The debit card breach raises significant concerns for India’s digital transformation in finance. Analysts have highlighted that insufficient infrastructure and cybersecurity measures could undermine the move towards a cashless economy, prompting calls for better fraud detection and management in the financial sector.
Why are some banks hesitant to disclose the details of the debit card breach?
Banks may hesitate to disclose details of the debit card breach out of concern for potential damage to their brand image. However, following new RBI regulations, they are now required to report cybersecurity incidents to avoid regulatory penalties.
What are Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) and how do they relate to the debit card breach?
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are sophisticated cyber threats that can infiltrate a network and remain undetected, potentially compromising sensitive data, such as debit card information. The recent breach highlights the need for banks to enhance their internal security to mitigate such risks.
How can customers verify if their cards are affected by the NPCI debit card breach?
Customers concerned about the NPCI debit card breach should contact their banks directly to inquire if their cards were affected. They can check their recent transaction history and report any suspicious activity to their bank for further investigation.
What measures can banks adopt to prevent future debit card breaches and ensure cybersecurity?
To prevent future debit card breaches, banks should implement robust cybersecurity frameworks, conduct regular audits, train staff on cybersecurity best practices, and adopt advanced technologies like point-to-point encryption for data security. Collaboration and information sharing within the finance sector can also bolster defenses against cyber threats.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| NPCI’s Address on Breach | The National Payments Corporation of India reassured cardholders about the recent debit card breach. |
| Number of Affected Customers | 641 customers reported unauthorized card usage in China and the USA. |
| Potentially Compromised Cards | About 3.2 million cards may have been at risk. |
| Auditing by PCI Security Council | The Payment Card Industry Security Council is currently auditing the situation. |
| Cybersecurity Reporting Mandate | The Reserve Bank of India now mandates immediate reporting of cybersecurity incidents. |
| Flaws in Cybersecurity | Expert analysts have pointed out serious flaws in the security systems. |
| Security Culture in Finance | The banking sector needs a culture of security intelligence sharing. |
| Digital Transformation Concerns | There are concerns regarding the infrastructure supporting a cashless economy. |
Summary
The recent debit card breach has raised significant concerns among cardholders, with the NPCI outlining the implications of this incident. Despite assertions that only a limited number of customers were directly impacted, the potential reach of the breach suggests a broader vulnerability in India’s financial systems. As organizations grapple with improving their cybersecurity frameworks and adhering to new compliance mandates, the need for robust security measures and a well-informed response strategy has never been more critical.